Cybersecurity management refers to an organization’s strategic efforts to safeguard information resources. It focuses on the ways businesses leverage their security assets, including software and IT security solutions, to safeguard business systems.
These resources are increasingly vulnerable to internal and external security threats such as industrial espionage, theft, fraud, and sabotage. Cybersecurity management must employ a variety of administrative, legal, technological, procedural, and employee practices to reduce organizations’ risk exposure.
Importance of risk management in cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is crucial to operational processes because it guards against the theft and destruction of data and IT systems, including personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), personal data, data pertaining to intellectual property, and information systems.
Your company cannot protect itself from data breaches without a cybersecurity strategy. In the absence of effective cybersecurity management practices, your organization becomes a prime target for cyber criminals.
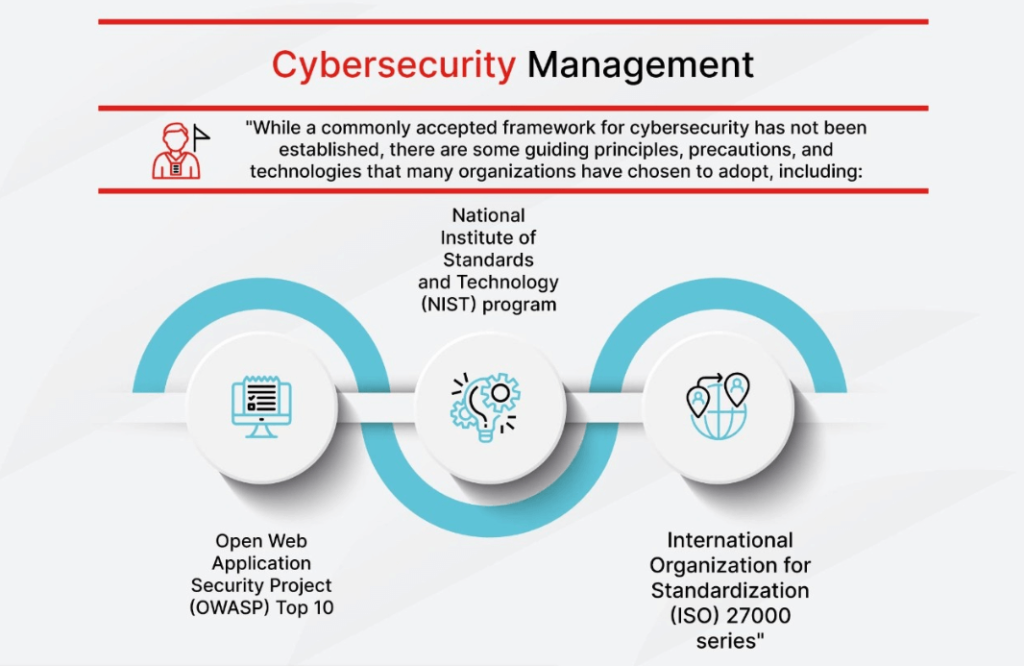
Framework of cybersecurity management
While a commonly accepted framework for cybersecurity has not been established, there are some guiding principles, precautions, and technologies that many organizations have chosen to adopt, including:
- Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) program
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 27000 series
These serve as the de facto frameworks for cybersecurity management, and they outline techniques and standards for protecting digital assets.
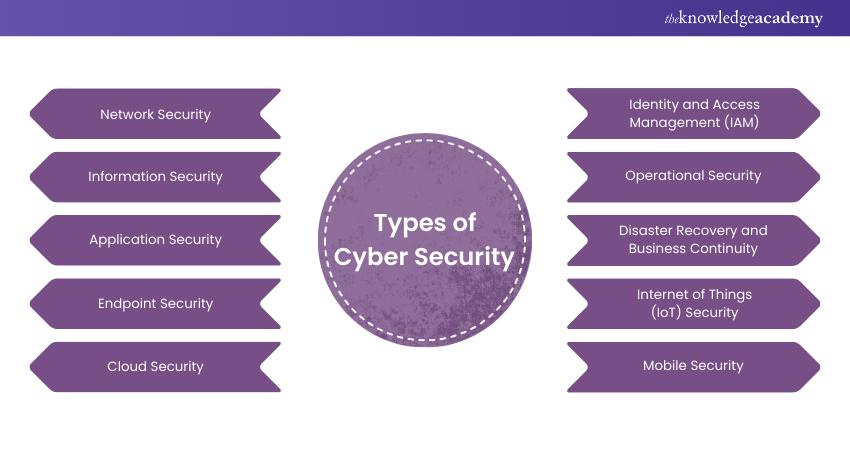
Types of Cybersecurity Management
Cybersecurity management encompasses a broad spectrum of activities aimed at protecting an organization’s digital assets. Here are some key types:
1. Risk Management
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing measures to reduce the impact of threats.
- Risk Transfer: Shifting risk to a third party (e.g., insurance).
2. Incident Response Management
- Incident Detection: Identifying security breaches or attacks.
- Incident Response: Implementing steps to contain and mitigate the damage.
- Incident Recovery: Restoring systems and data to normal operations.
3. Access Management
- Identity and Access Management : Controlling who can access systems and data.
- Authentication: Verifying user identities.
- Authorization: Determining user permissions.
4. Data Security Management
- Data Classification: Categorizing data based on sensitivity.
- Data Encryption: Protecting data with cryptographic methods.
- Data Loss Prevention : Preventing unauthorized data transfer.
5. Network Security Management
- Firewall: Controlling network traffic.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems : Identifying and blocking attacks.
- Virtual Private Networks : Secure remote access.
6. Application Security Management
- Secure Coding Practices: Developing software with security in mind.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Identifying weaknesses in applications.
- Web Application Firewalls : Protecting web applications.
7. Cloud Security Management
- Infrastructure as a Service Security: Protecting cloud infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service Security: Securing cloud platforms.
- Software as a Service Security: Protecting cloud applications.
8. Compliance Management
- Adhering to Regulations: Meeting industry-specific standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Auditing and Monitoring: Ensuring compliance through regular checks.
9. Security Awareness and Training
- Employee Education: Raising awareness about cybersecurity threats.
- Phishing Simulations: Testing employee vigilance.
- Best Practices Training: Teaching secure behaviors.
10. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
- Developing Plans: Creating strategies for business continuity.
- Testing and Exercising: Ensuring plans are effective.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Protecting critical data.
Cybersecurity Management Benefits
An effective cybersecurity management policy takes into account the risks that exist for an organization’s resources. Those that administer the program formalize processes and procedures. Once vulnerabilities are found, the management policy will outline solutions to stop malicious code from infiltrating the organization’s perimeter defense systems, servers, and desktops. It also describes how to deploy mitigation measures and who is in charge in the event of a breach.
A cybersecurity management program provides an organization with critical services, such as:
- Designing and implementing an efficient enterprise security architecture
- Mitigating advanced threats
- Securing Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Providing security intelligence
Some external cybersecurity management services also provide IT security consulting to help companies craft the best strategies to protect their environments now and in the future.
Difference between cybersecurity and cybersecurity management
What is cybersecurity management? A cybersecurity management system is different from cybersecurity itself. Cybersecurity management focuses on ways to organize security assets, people, and processes, while cybersecurity is a general label for protecting an organization’s digital infrastructure.
In this cybersecurity management definition, the act of managing cybersecurity involves both technical strategy and shaping company culture.
6 Best Practices in Cybersecurity Management
Here are six tried-and-tested best practices for cybersecurity management.
1. Understand your IT assets and environment
Effective cybersecurity management requires in-depth knowledge of the IT environments and resources within your firm, including all data and other digital assets, BYOD devices, systems, networks, third-party services, technologies, endpoints, and other relevant items.
Awareness of all the elements of your IT landscape is critical, especially because each facet of your network can be used to penetrate your system. Also, it is imperative that you assess your assets and monitor your IT environment continuously.
2. Deploy a risk management strategy
Managing risk without a well-thought-out and effective cybersecurity risk management strategy is counterproductive. Organizations must create sound strategies and plans to keep them up-to-date.
Prior to planning, determine your level of risk tolerance and then create a risk profile. Include roles for all employees and key stakeholders, incident response and escalation strategies, and other relevant information.
3. Make cybersecurity risk management an element of company culture
Even well-crafted cybersecurity risk management policies and processes are useless if they are not properly implemented throughout the firm. So make sure to convey your ideas, plans, and procedures to all parties involved. Integrate cybersecurity risk management within the values and culture of the company. Each party involved in managing cyber threats needs to be aware of, understand, and embrace their responsibilities.
4. Use continuous, adaptive, and actionable risk assessments
Risk identification and assessment are two of the most crucial components of risk management. Risks associated with cybersecurity are always changing. A change in company procedures or the introduction of new technologies, for example, can change your risks significantly. As a result, the organization’s general risk assessment has to be adjusted. To ensure effective security, your procedures must be continuously assessed for deficiencies—and improved.
Risk assessments are also critical because they provide the business with information about where vulnerabilities currently exist, as well as which threats are on the horizon.
5. Implement strict security protocols
Effective risk mitigation requires a security system that is both comprehensive and user-friendly. Here are a few techniques:
- Use a web application firewall (WAF) managed and situated at the network’s edge to keep track of traffic, offer immediate and actionable information, and continuously protect against known and unknown threats.
- Extend security to BYOD devices and all other hardware in your IT environment.
- Implement stringent security procedures for remote employees.
- When possible, use automatic patching to keep all security systems up-to-date.
- Implement stringent access controls and authentication policies.
- Consolidate systems and data whenever possible. Data that is segregated and dispersed is more difficult to manage and secure.
- Set up a consistent, reliable backup system.
6. Enhance visibility into your network
Visibility into all areas of your network is critical to preventing and mitigating cybersecurity incidents. Factors like insider threats, third-party components with built-in vulnerabilities, and human error can endanger your environment. Real-time and trustworthy visibility into your organization’s risk profile is essential.
Cybersecurity Risk Management

Here are some of the current trends impacting cybersecurity risk management.
Risks in the digital supply chain
Attacks on the digital supply chain can yield a significant return on investment, as cyber criminals have come to realize. More dangers are anticipated as new vulnerabilities proliferate throughout the supply chain. This is primarily because third parties, which have varying levels of cybersecurity, have become a primary attack vector for bad actors.
For example, even though your environment is relatively secure, a criminal may use a provider in your supply chain with access to your system as a conduit to infiltrate your network.
Expanding attack surface
Attack surfaces on enterprise systems are growing. Risks related to IoT, open-source software, cloud computing, complicated digital supply chains, social media, and other technologies are leaving many organizations exposed to attackers. To handle a wider range of security exposures, companies must look beyond conventional security monitoring, detection, and response methodologies.
This may involve developing internal and external business systems, as well as automating security gap identification. Chief information security officers (CISOs) can use external attack surface management (EASM) technologies, digital risk protection services (DRPS), and cyber asset attack surface management (CAASM) to implement these kinds of systems.
Wider distribution of cybersecurity responsibilities
Executives now want more adaptive security as enterprise cybersecurity demands and expectations mature. To do this, it is best to spread cybersecurity decision-making, accountability, and responsibility throughout the organization, rather than keeping them centralized.
This is particularly important because of the increasing size and complexity of organizations, which may make it difficult for a single person or small team to handle cybersecurity management on their own.
Components of a Cyber Security Management System
Each of the following components is critical to the overall effectiveness of the cybersecurity management system.
- Risk Assessment
The first step in developing a cybersecurity management system is to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities to the organization’s systems and data. This includes identifying the assets that need protection, assessing the likelihood of a threat, and estimating the potential impact of a successful cyber-attack. This information is used to prioritize cybersecurity measures and allocate resources effectively.
- Security policies and procedures
Once risks have been identified, it is essential to develop security policies and procedures that are designed to protect against them. Security policies and procedures should be comprehensive and address all aspects of cyber-security, from access controls and data encryption to incident response and recovery. Policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure they remain effective against emerging threats.
- Employee education and training
Employees are often the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain. Cybercriminals use social engineering techniques to gain access to systems and data by exploiting human vulnerabilities. Therefore, providing education and training on cybersecurity best practices is essential to reducing the risk of cyber-attacks. Employees should be trained on how to identify and respond to phishing attacks, how to use strong passwords, and how to recognize other common types of cyber threats.
The Top 6 Cybersecurity Management Solutions
Cybersecurity risk management solutions are used to gain visibility over your entire network and to understand the risks that your organization may be susceptible to. Risk management tools can cover a wide range of risks – from technological misconfigurations to data security incidents, such as credential compromise.
1.Crowdstrike Falcon Intelligence Premium
Crowdstrike is a cybersecurity solutions provider that uses real-time indicators of compromise (IOCs), threat intelligence, and data enrichment to identify threats to your network. Falcon Intelligence Premium is a cloud-based platform that gives you in-depth context and actionable intelligence regarding cybersecurity threats. The company was founded in 2011, and is based in Austin, TX.
Crowdstrike Falcon Intelligence Premium Features:
- Automatically scans the internet and social media sites to identify suspicious activity
- Connected to a global IOC database to accurately identify new and emerging threats
- Automated investigations reduce the human time and expertise required
- Generates custom reports for a range of shareholders, including technical reports and business impact reports for C-suite
- Integrates effectively with the other elements of the Falcon platform
- Constantly monitors for DDoS and botnet attacks
2. CURA Enterprise Risk Management
Based in Johannesburg, South Africa, CURA is a governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) solutions provider for enterprise environments. Their Enterprise Risk Management solution streamlines risk management by integrating risk decisions within your business processes. The solution can effectively communicate risk, allowing you to make smart and secure decisions. You are able to set goals and objectives, then monitor your performance in relation to these targets.
CURA Enterprise Risk Management Features:
- Supports multiple frameworks and methodologies to ensure compliance with data protection regulations – Sarbanes-Oxley, COSO, ISO31000, and others
- Real-time network visibility from interactive dashboard and reports
- Platform can be granularly configured so that you can tailor the risk management process
- Alert tools to warn of tasks, actions, and escalations
- Comprehensive audit trails
3.LogicManager Integrated Risk Management
LogicManager is a Boston-based risk management company that has been in operation since 2005. Their IRM solution provides visibility across your network, identifying the risks that you face. This allows you to anticipate future threats, improve business performance, and mitigate current dangers. LogicManager helps to separate the strands of interconnected risk, giving you clarity and allowing you to act with precision.
LogicManager Integrated Risk Management Software Features:
- Out-of-the-box heat maps, top risk summaries, and risk control matrices accessible through a customizable dashboard
- Risk identification and prioritization
- Highlights departmental relationships and dependencies
- Continued, real-time risk intelligence
- Assign pre-built and customizable controls to identified vulnerabilities
- Scalable solution that ingests data from across your network
4.ManageEngine Vulnerability Manger
ManageEngine has developed a broad suite of cybersecurity tools that include access management, auditing, and endpoint security products, as well as solutions in many other areas. Vulnerability Manager is their tool for identifying, assessing, and mitigating the risks facing your network. The solution is designed to work across multiple operating systems and to gather data from endpoints across your entire network.
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manger Features:
- Assess and prioritize network vulnerabilities based on factors like exploitability, age, frequency, severity, and patch availability
- Optimize system security – enforce complex passwords, access management, and memory protection features
- Adhere to audit and compliance requirements
- Deploy pre-built scripts to zero-day threats
- Identify and remove high risk software – remote desktop sharing, end-of-life, and peer-to-peer applications
- Automate the testing and deployment of security patches
5. Onspring Risk Management Enterprise Solution
Onspring is a Kansas-based GRC and workflow automation provider. The company was founded in 2010 and today produces internal threat management, GRC, third-party risk management, and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) tools. The Risk Management Enterprise Solution empowers organizations to gain clarity into the risks they face, and to respond appropriately and effectively. The solution empowers you to conduct risk assessments across your network, to understand the likelihood and impact of various risks.
Onspring Risk Management Enterprise Solution Features:
- Centralized risk register makes it easy to organize, understand, and compare cyber risks
- Real-time data analysis to accurately calculate potential risk
- Monitor financial impact of potential risks to understand how significant the threat is
- Auditing and reporting features make it easy to communicate findings with key stakeholders
- Integrate reports with other business units and external data feeds
6. Qualys Cloud Platform
Qualys is a California-based provider of cloud-based security and compliance solutions. The Qualys Cloud Platform gives organizations continuous visibility and assessment of global IT, security, and compliance posture. The platform has built-in threat prioritization and remediation features (such as automated patching), to protect your digital environment. Qualys monitors your cloud and on-premises environments and devices to provide extensive visibility with a good degree of accuracy.
Qualys Cloud Platform Features:
- Monitors all the devices on your network, including mobile endpoints, workstations, containers, and cloud instances
- Continuous monitoring means that admins can be notified at the earliest opportunity
- Comprehensive analysis adds context to risk data so that you can fully understand the security implementations of each incident
- Customizable dashboard allows you to highlight the data that is important to your organization
- Helps organizations to adhere to CIS and PCI policies
Challenges in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving landscape, presenting numerous challenges for individuals and organizations alike. Here are some of the most significant:
1. The Ever-Evolving Threat Landscape
- New threats emerging constantly: Cybercriminals are always developing new techniques and tools.
- Sophistication of attacks: Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly complex and targeted.
2. Shortage of Cybersecurity Professionals
- Talent gap: Difficulty finding skilled cybersecurity experts.
- High demand, low supply: Competition for qualified professionals is intense.
3. Increasing Complexity of IT Environments
- Cloud computing: While offering benefits, it also introduces new security challenges.
- IoT devices: The proliferation of connected devices expands the attack surface.
4. Human Error
- Accidental data breaches: Employees can inadvertently compromise security.
- Social engineering attacks: Phishing and other social engineering tactics are effective.
5. Economic Impact
- Financial losses: Cyberattacks can result in significant financial damages.
- Reputation damage: Security breaches can harm a company’s reputation.
6. Regulatory Compliance
- Complex regulations: Adhering to various cybersecurity laws can be burdensome.
- Penalties for non-compliance: Failure to comply can lead to severe consequences.
7. Supply Chain Attacks
- Vulnerabilities in the supply chain: Compromised third-party vendors can expose organizations to risk.
- Difficulty in assessing supplier security: Evaluating the security posture of suppliers is challenging.
8. Ransomware
- Disruption of operations: Ransomware attacks can cripple businesses.
- Data loss: Sensitive data may be stolen or destroyed.
9. Data Privacy
- Protecting personal information: Safeguarding sensitive data is crucial.
- Compliance with regulations: Meeting data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA is essential.
10. Emerging Technologies
- AI and machine learning: While offering potential benefits, these technologies can also be used for malicious purposes.
- Quantum computing: Could break current encryption methods, requiring new security solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cybersecurity is a complex challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the evolving threat landscape, investing in people, technology, and processes, and fostering a culture of security, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against cyberattacks.
While technology plays a crucial role, a truly effective cybersecurity strategy hinges on a combination of robust technology, human expertise, and a strong organizational culture.
FAQs
Cybersecurity management refers to an organization’s strategic efforts to safeguard information resources. It focuses on the ways businesses leverage their security assets, including software and IT security solutions, to safeguard business systems.
An effective cybersecurity management policy takes into account the risks that exist for an organization’s resources. Those that administer the program formalize processes and procedures. Once vulnerabilities are found, the management policy will outline solutions to stop malicious code from infiltrating the organization’s perimeter defense systems, servers, and desktops.
